学习一个常用的UI状态架构
喜马拉雅视频教程07-学习一个常用的UI状态架构
接下来呢,我们要学习一个UI状态常用的框架,自己写。 在前面的课程里面,我们只有一种状态,就是数据请求成功。其实,我们一个页面是有多种状态的。 比如说:
- 数据加载中
- 数据加载成功数据加载失败
- 数据为空
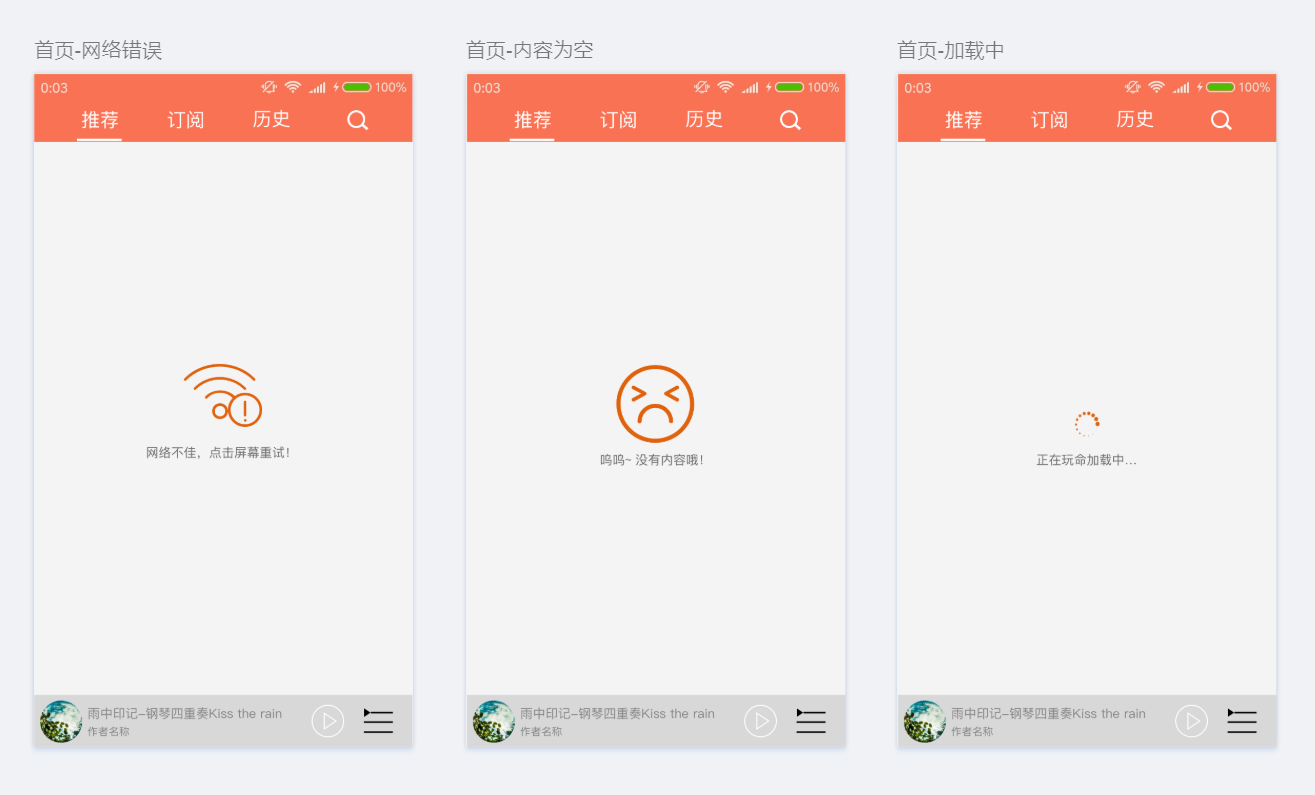
怎么解决这个问题呢? 使用面向对象的思想,我们可以创建一个类来管理这些状态。不同的状态去加载不同的界面即可。 对吧! 具体怎么实现呢?
先上代码,看不懂去看视频吧:
package com.sunofbeaches.himalaya.views;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.annotation.NonNull;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.FrameLayout;
import com.sunofbeaches.himalaya.R;
import com.sunofbeaches.himalaya.base.BaseApplication;
/**
* Created by TrillGates on 2019/1/2.
* God bless my code!
*/
public abstract class UILoader extends FrameLayout {
private View mLoadingView;
private View mSuccessView;
private View mNetworkErrorView;
private View mEmptyView;
private OnRetryClickListener mOnRetryClickListener = null;
public enum UIStatus {
LOADING, SUCCESS, NETWORK_ERROR, EMPTY, NONE
}
public UIStatus mCurrentStatus = UIStatus.NONE;
public UILoader(@NonNull Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public UILoader(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public UILoader(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//
init();
}
public void updateStatus(UIStatus status) {
mCurrentStatus = status;
//更新UI一定要在主线程上。
BaseApplication.getHandler().post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
switchUIByCurrentStatus();
}
});
}
/**
* 初始化UI
*/
private void init() {
switchUIByCurrentStatus();
}
private void switchUIByCurrentStatus() {
//加载中
if (mLoadingView == null) {
mLoadingView = getLoadingView();
addView(mLoadingView);
}
//根据状态设置是否可见
mLoadingView.setVisibility(mCurrentStatus == UIStatus.LOADING ? VISIBLE : GONE);
//成功
if (mSuccessView == null) {
mSuccessView = getSuccessView(this);
addView(mSuccessView);
}
//根据状态设置是否可见
mSuccessView.setVisibility(mCurrentStatus == UIStatus.SUCCESS ? VISIBLE : GONE);
//网路错误页面
if (mNetworkErrorView == null) {
mNetworkErrorView = getNetworkErrorView();
addView(mNetworkErrorView);
}
//根据状态设置是否可见
mNetworkErrorView.setVisibility(mCurrentStatus == UIStatus.NETWORK_ERROR ? VISIBLE : GONE);
//数据为空的界面
if (mEmptyView == null) {
mEmptyView = getEmptyView();
addView(mEmptyView);
}
//根据状态设置是否可见
mEmptyView.setVisibility(mCurrentStatus == UIStatus.EMPTY ? VISIBLE : GONE);
}
protected View getEmptyView() {
return LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.fragment_empty_view, this, false);
}
protected View getNetworkErrorView() {
View networkErrorView = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.fragment_error_view, this, false);
networkErrorView.findViewById(R.id.network_error_icon).setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//重新获取数据
if (mOnRetryClickListener != null) {
mOnRetryClickListener.onRetryClick();
}
}
});
return networkErrorView;
}
protected abstract View getSuccessView(ViewGroup container);
protected View getLoadingView() {
return LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.fragment_loading_view, this, false);
}
public void setOnRetryClickListener(OnRetryClickListener listener) {
this.mOnRetryClickListener = listener;
}
public interface OnRetryClickListener {
void onRetryClick();
}
}
继承自Framelayout,说明这是一个View,哪里需要显示,直接创建,扔进去即可。
在于要什么内容,在创建的时候强制要求你实现。
如果你不满意现有的内容,复写相关的状态方法即可。
更新UI只要调用一下状态更新即可。
具体请看视频内容吧!